Release time:2024-06-24
Recently, the team of Ocean Communication and Navigation Technology from the School of Marine Science and Technology, Tianjin University, has made new progress in underwater navigation, with a paper titled "A Robust Graph-based Bathymetric Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Approach for AUVs" published online in the top journal IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering in the field of marine engineering. Dalong Zhang, a 2021 graduate student, is the first author of the paper, and Associate Professor Shuai Chang of the Department of Marine Technology is the corresponding author.
Underwater navigation and positioning technology is one of the core technologies of underwater autonomous vehicles, and it is also the bottleneck technology that currently limits the long-distance, long-endurance, high-precision safe navigation and high-precision operation of underwater vehicles. In general underwater navigation environments without satellite navigation and acoustic positioning systems, the Earth's physical fields become an important source of information for providing a stable spatial position reference for underwater vehicles and achieving convergence of navigation errors. The team used the seafloor topography as the reference field and studied a robust graph optimization simultaneous localization and mapping algorithm for underwater vehicles operating in general underwater environments without prior information. This provides reliable positioning technology support for underwater vehicles in underwater measurement and target search operations.
This study quantitatively analyzes the influence of the mechanism for constructing submarine terrain multi-beam measurement sub-maps on data association, and clarifies several criteria for real-time construction of underwater terrain sub-maps. Based on these criteria, a two-step data association method is proposed, which uses an innovative method for extracting key features from multi-beam terrain measurement data, robust coarse alignment based on feature vectors, and a fine alignment method with error matching identification in a graph optimization SLAM framework to construct the front-end factor graph.
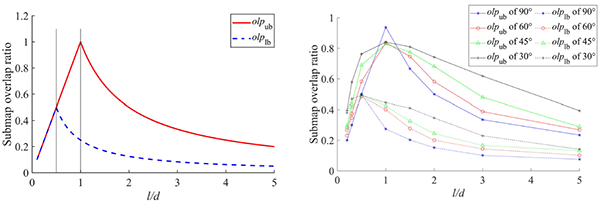
Picture 1 Analysis of the Impact of Multi-Beam Submap Division Mechanism on Data Association
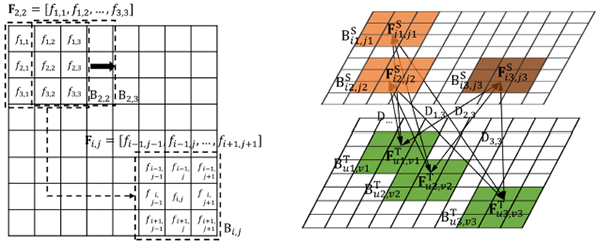
Picture 2 Robust coarse alignment of multi-beam terrain data based on key feature extraction and feature vector
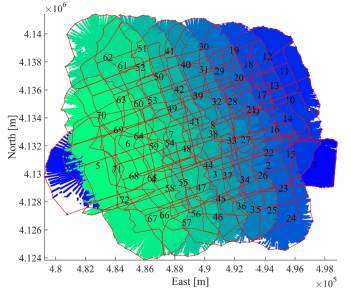
Picture 3 Navigation Position Error Statistics and Topographic Maps
In order to ensure the accuracy of the SLAM position estimation and terrain map construction, and to filter out the effects of outliers, a robust backend optimizer based on the Frechet distance was developed, which automatically identifies and excludes incorrect data association factors in the optimization process, achieving robust navigation state estimation and high consistency in terrain map construction. The research results show that, with the help of this method, using a low-cost navigation system, an accuracy of less than 100 meters can be achieved in a completely underwater navigation path of over 20km. In the context of the rapid progress of marine autonomous vehicle technology and the increasing diversification of its application scenarios, this research has significant potential for use in a variety of scenarios, such as underwater environment exploration and target search.
Reference
D. Zhang, S. Chang, et al. "A Robust Graph-Based Bathymetric Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Approach for AUVs," in IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, doi: 10.1109/JOE.2024.3401969.